At the time of writing, Volkswagen sells six fully electric cars in the UK. The latest EV to join the German marque’s expanding range is the ID.7 Tourer.
This guide offers a broad overview of what you need to know about buying an electric Volkswagen right now. We will aim to update the page regularly as new electric Volkswagens are introduced.
Got any additional questions? Let us know in the comments and we will endeavour to help.
Buying an electric Volkswagen

Which fully electric cars does Volkswagen sell?
Volkswagen offers six fully electric cars in the UK: the ID.3 (family hatchback), ID.4 (compact SUV), ID.5 (SUV coupe), ID.7 (executive hatchback), ID.7 Tourer (large estate) and ID.Buzz (people carrier).
Which Volkswagen electric cars are coming soon?
Volkswagen has promised to launch 10 new electric cars by 2026, the first of which is likely to be the ID.2all. Similar in size to a Golf, this model is expected to cost around £22,000 and offer up to 280 miles of range. It will also spawn a sporty version called the ID.GTI.
A long wheelbase version of the ID.Buzz is also due in 2025, along with a sporty GTX version of the fashionable electric MPV.
What is Volkswagen’s electric car brand called?
Volkswagen’s electric car brand is called ID. In 2020, the company said it stands for ‘intelligent design, identity and visionary technologies’, although this is more often shortened simply to ‘intelligent design’.

What is the warranty on a Volkswagen electric car battery?
Volkswagen electric car batteries are covered for eight years or 100,000 miles, whichever comes first. The cars are covered by the marque’s standard three-year or 60,000-mile warranty.
Where can you buy a Volkswagen electric car?
You can buy a new Volkswagen electric car from your nearest Volkswagen dealer.
How much do Volkswagen electric cars cost?
With prices starting from around £31,000, the ID.3 is currently the cheapest Volkswagen electric car on sale, although the forthcoming ID.2all is expected to undercut it by around £10,000. Next up at the moment is the ID.4, which starts from around £44,500.
The ID.5 is a tad more expensive at £46,000, while the ID.7 and ID.7 Tourer start from £51,500 and £52,500 respectively. Finally, life with an ID.Buzz costs from around £59,000.
Charging an electric Volkswagen

What type of plug do Volkswagen EVs use?
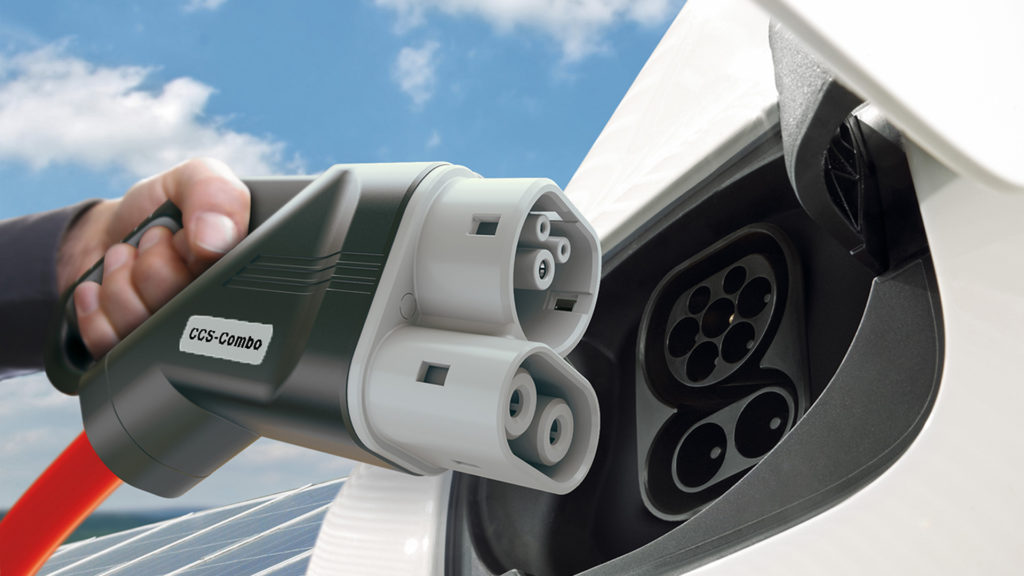
Volkswagen electric cars use a CCS (Combo Rapid Charge) and seven-pin Type 2 plug.
What charging equipment comes as standard with a Volkswagen electric car?
Volkswagen electric cars come with a Type 2 (Mode 3) charging cable for public charging. A Mode 2 charging cable for home charging is available as an optional extra.
Can Volkswagen electric cars use rapid chargers?
Yes, all Volkswagen electric cars can use rapid chargers, but the maximum charging speed will depend on the model. For example, an ID.7 with an 86kWh battery pack can charge at speeds of up to 200kW, while the ID.3’s peak is 170kW.
Can Volkswagen electric cars use Ionity chargers?
Yes, all ID electric cars can use the Ionity ultra-rapid charging network. Indeed, Volkswagen was one of the founding partners in creating the Ionity network, along with BMW, Ford, Hyundai and Mercedes-Benz.
Where is the charging point located on a Volkswagen electric car?
The charging point on the ID.3, ID.4, ID.5, ID.7 and ID.7 Tourer is located on the driver’s side rear wing, above the rear wheel. On the ID.Buzz, it’s also on the driver’s side rear wing, but positioned a little lower, between the rear wheel and the back bumper.
Which charge partner does Volkswagen work with?
Volkswagen works with Ohme, OVO and BP Pulse to deliver a range of charging solutions, both at home and on the move.

What is Volkswagen wallbox called?
There isn’t a specific Volkswagen-branded wallbox charger (see below).
What wallbox options does Volkswagen offer?
Volkswagen recommends the use of Ohme’s home chargers, and OVO as a green energy provider. There are two wallboxes available: Ohme Home Pro for 7kW tethered charging and Ohme ePod for 7kW untethered home charging.
Do you get a free wallbox when you buy a new Volkswagen electric car?
No, you will have to pay extra for an Ohme home charger. The Home Pro unit costs £975, while the ePod is cheaper at £925. Both these prices include installation.
What is the Volkswagen charging service?
Volkswagen’s charging service is called We Charge. There are three plans to choose from, each one tailored to specific needs. For example, We Charge Free has no monthly fee and prices ranging from 69p to 85p per kWh.
The mid-tier We Charge Go costs £5.49 a month and has a tariff of 53p to 85p per kWh, while We Charge Plus costs £13.99 a month but offers the lowest prices, at 53p to 69p per kWh.
Do Volkswagen electric cars have an on-board DC charger?
Yes, all Volkswagen ID models are fitted with an 11kW on-board charger.
What is the maximum charging speed of a Volkswagen electric car?
The maximum charging speed of a Volkswagen electric car depends on the model and battery size. For example, the ID.3 with a 77kWh battery pack has a maximum charging rate of 170kWh, while the ID.4 maxes out at 125kW, even with the 77kWh battery.
The arrival of the GTX model has boosted the ID.5’s charging speed to 175kW, while the ID.7 offers a peak speed of 200kW. Lastly, the ID.Buzz has a maximum charging rate of 170kW.
Driving an electric Volkswagen

What is the range of a Volkswagen electric car?
Volkswagen ID.3: up to 334 miles
Volkswagen ID.4: up to 349 miles
Volkswagen ID.5: up to 344 miles
Volkswagen ID.7: up to 436 miles
Volkswagen ID.7 Tourer: up to 424 miles
Volkswagen ID.Buzz: up to 293 miles
Please note: these figures are the maximum (combined) range for each model. The exact numbers will vary depending on power output, battery capacity, options selected and wheel size.
What is the Volkswagen electric car smartphone app called?
Volkswagen’s smartphone app is simply called ‘Volkswagen’. Using VW Connect/We Connect, ID owners can access real-time traffic information, pre-heat or pre-cool their car’s cabin, get a vehicle health report and an array of other features.

How many Volkswagen dealers are there and do they offer free charging for owners?
There are approximately 180 Volkswagen dealers in the UK, none of which offer free charging for owners. Click here to discover where you can still charge an electric car for free.
Does Volkswagen sat-nav show charging point locations and availability?
Yes, the EV route planner in Volkswagen’s sat-nav system shows charging point locations and availability.
ALSO READ:
Volkswagen USA brings home a classic Golf after 37 years